The Goals define the future outcome that needs to be achieved. Each Goal contributes to the achievement of the Vision Statement. While the Vision Statement needs to be short, the Goals can go into detail about the results to be attained, building on the possible solutions to the previously described impediments described in the Baseline. All Goals should be S.M.A.R.T., meaning specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time bound.
SMART Goals
Specific: Goals should be concrete. They should be defined in an explicit and unequivocal way, with no room for interpretation. Tip: a good starting point is defining Goals based on the Six Ws (Who, What, When, Where, Why, HoW).
Measurable: Goals should include criteria that will help assessing the progress made and whether goals were reached.
Attainable: Goals should be realistic but still challenging. Goals that are too easy or too difficult to accomplish could result in a demotivation of stakeholders.
Relevant: Goals should be meaningful. They should contribute to the completion of the trade facilitation vision established.
Time-bound: Goals should be framed in time. For that purpose, goals can include deadlines. Tip: Defining a time-frame might be useful even before defining a goal. Stakeholders should start answering the question: what could be reached in this particular period of time? It helps managing expectations and ensures that discussions among stakeholders would stay realistic. Within a given period of time it is easier to figure out what is possible and what not.
For instance:
“Goal 1: To reduce transaction time by (XX %) through establishing a paperless trade for exports environment by (date). Traders will be allowed to submit all documents requested for export electronically.”
“Goal 2: To reduce release times by (XX %) for imports through upgrading the Customs risk management system and implementing risk management systems in other Agencies dealing with inspections such as the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Heath by (date).”
Identifying goal performance indicators
The Roadmap should establish performance indicators to assess the achievement of the Goals (Goals Performance Indicators). These indicators are references establishing what conditions demonstrate that a Goal was successfully achieved or an action effectively implemented. In other words, indicators demonstrate results.
Indicators need to be quantifiable; they need to have a unit of measurement. Some examples of measurement are time for clearance of imports, transport costs of a container or number of inspections, among others. A Goal Performance Indicator (GPI) may include reference to the baselines identified earlier in the Roadmap. For instance, a decrease in the costs of transport will need to be measured against the actual cost at the time the Roadmap was drafted. Thus, baselines need to be included and properly documented if there are to be used as part of the performance indicators.
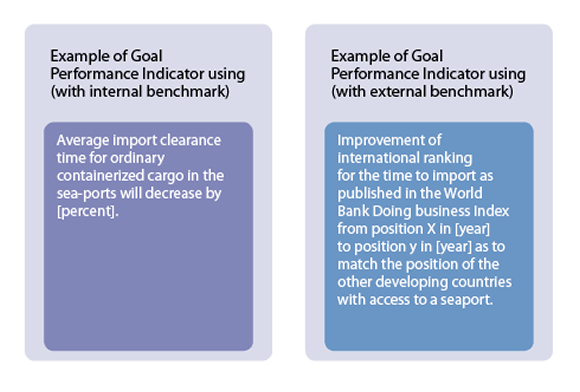
Goals Performance Indicators may also (or alternatively) use international benchmarks that compare the country’s situation in relation to other countries. These benchmarks are particularly useful if Goals of the Roadmap aim at improving the trading situation of the country in comparison with other countries.
International rankings regarding logistics and other trade facilitation indicators are a good reference point to be used as Benchmarks. For instance, the rankings of the World Bank Doing Business with its Trading Across Borders Indicators as well as the Logistics Performance Index can be used as reference points.
Figure 1: Example of Goal Performance Indicator with internal and external benchmarks |
However, international rankings should always be used prudently as performance indicators. It is important to put them in perspective. Firstly, the methodology used to gather data might not always be based on objective criteria.
In the process of setting up external Goal Performance Indicators using a Benchmark, a country should consider the following questions:
- What is my country’s current position? How does my country score in the different aspects taken into consideration?
- Which countries are in a comparable position to assess whether the Roadmap Goals are being implemented successfully?
- Which countries have developed trade facilitation best practices that I would like to replicate?
- What is the position of the countries I am benchmarking against?
- In which position should my country be in the following [number of] years? How much should my country score in the following [number of] years?